Streaming data from Kafka to Elasticsearch is easy with Kafka Connect - you can see how in this tutorial and video.
One of the things that sometimes causes issues though is how to get location data correctly indexed into Elasticsearch as geo_point fields to enable all that lovely location analysis. Unlike data types like dates and numerics, Elasticsearch’s Dynamic Field Mapping won’t automagically pick up geo_point data, and so you have to do two things:
-
Declare the index mapping in full, or use a dynamic template to tell Elasticsearch to create new fields as a
geo_pointif they match the given pattern -
Make sure that your
geo_pointsource data is in the structure that Elasticsearch requires, covered in full here but basically:-
object/struct
"location": { "lat": 41.12, "lon": -71.34 }the field names are case sensitive -
string
"location": "41.12,-71.34" -
array
"location": [ -71.34, 41.12 ] -
plus geohash and WKT POINT.
-
How? 🔗
To get the data into the necessary format you can use ksqlDB to wrangle it, which is what I show below.
You could also use Kafka Connect’s Single Message Transform feature but no existing transformation exists that I’m aware of that does the necessary - drop me a line if you write one!
Example 🔗
Here’s a worked example showing how to do this. It assumes that you’ve got a source topic with latitude and longitude, in this case it’s already as a struct but with the incorrect capitalisation ("Location": { "Lat": 43.7575119, "Lon": 11.2921363 }).
-
Populate source topic with the sample data:
kafkacat -b localhost:9092 -P -t input_topic <<EOF { "ID": "7d6203f4-3ae7-4daa-af03-71f98d619f7e", "Timestamp": "2020-11-02T12:05:57.87639003Z", "Type": "CREATION", "PlaceType": "home", "Location": { "Lat": 43.7575119, "Lon": 11.2921363 }, "Created": "2020-11-02T12:05:57.876390266Z", "LastUpdated": "2020-11-02T12:05:57.876390398Z" } EOF -
Taking a source topic of
source, declare the ksqlDBSTREAMobject (which is basically Kafka topic with a schema overlaid):CREATE STREAM SOURCE_STREAM (ID VARCHAR, Timestamp VARCHAR, Type VARCHAR, PlaceType VARCHAR, Location STRUCT<Lat DOUBLE, Lon DOUBLE>, Created VARCHAR, LastUpdated VARCHAR) WITH (KAFKA_TOPIC='input_topic', VALUE_FORMAT='JSON'); -
Confirm that the stream’s schema is valid by selecting fields from the first message:
ksql> SET 'auto.offset.reset' = 'earliest'; > Successfully changed local property 'auto.offset.reset' to 'earliest'. Use the UNSET command to revert your change. ksql> SELECT ID, PLACETYPE, LOCATION->LAT, LOCATION->LON FROM SOURCE_STREAM EMIT CHANGES LIMIT 1; +---------------------------------------+----------+-----------+-----------+ |ID |PLACETYPE |LAT |LON | +---------------------------------------+----------+-----------+-----------+ |7d6203f4-3ae7-4daa-af03-71f98d619f7e |home |43.7575119 |11.2921363 | Limit Reached Query terminated -
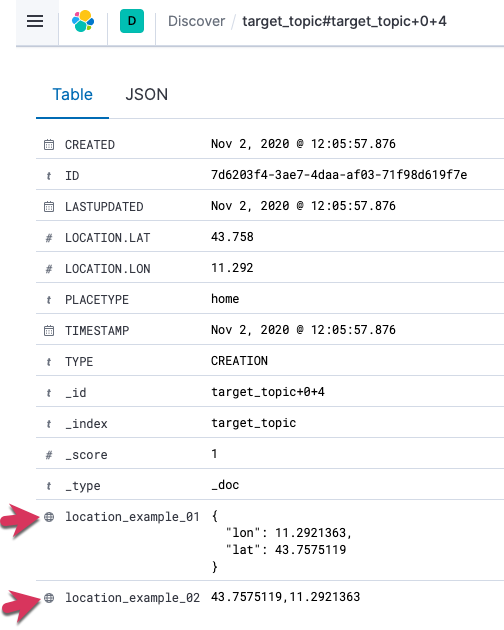
Create a target stream, mapping the lat/lon fields to lower-case names. Here I’m also showing the alternative approach of concatenating them, which Elasticsearch will also accept:
CREATE STREAM TARGET_STREAM WITH (KAFKA_TOPIC='target_topic') AS SELECT *, STRUCT("lat" := LOCATION->LAT, "lon":= LOCATION->LON) AS "location_example_01", CAST(LOCATION->LAT AS VARCHAR) + ',' + CAST(LOCATION->LON AS VARCHAR) AS "location_example_02" FROM SOURCE_STREAM; -
Create an index template for Elasticsearch if the index does not already have the
geo_pointmapping declared. Here it’ll match any index created that begins withtargetcurl --silent --show-error -XPUT -H 'Content-Type: application/json' \ http://localhost:9200/_index_template/rmoff_template01/ \ -d'{ "index_patterns": [ "target*" ], "template": { "mappings": { "properties": { "location_example_01": { "type": "geo_point" }, "location_example_02": { "type": "geo_point" } } } } }' -
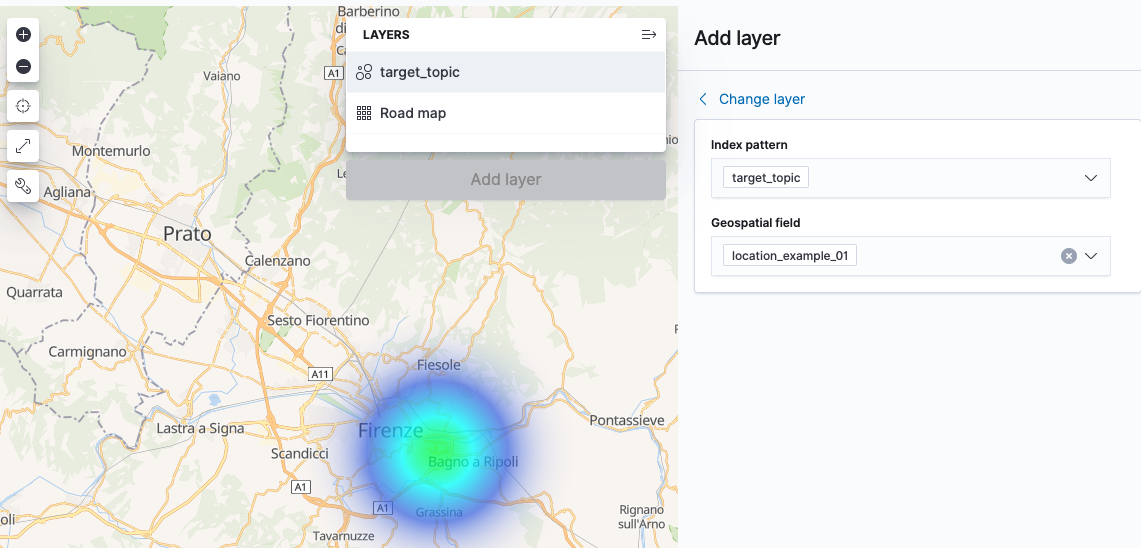
Stream the data from Kafka to Elasticsearch using Kafka Connect. You can do configure this using the native Kafka Connect REST API, or do it directly from ksqlDB itself:
CREATE SINK CONNECTOR SINK_ELASTIC_01 WITH ( 'connector.class' = 'io.confluent.connect.elasticsearch.ElasticsearchSinkConnector', 'topics' = 'target_topic', 'key.converter' = 'org.apache.kafka.connect.storage.StringConverter', 'value.converter' = 'org.apache.kafka.connect.json.JsonConverter', 'value.converter.schemas.enable' = 'false', 'connection.url' = 'http://elasticsearch:9200', 'type.name' = '_doc', 'key.ignore' = 'true', 'schema.ignore' = 'true'); -
Inspect the mappings in the new Elasticsearch index
curl -XGET --silent --show-error http://localhost:9200"/target_topic/_mappings" | jq '.' { "target_topic": { "mappings": { "properties": { "CREATED": { "type": "date" }, "ID": { "type": "text", "fields": { "keyword": { "type": "keyword", "ignore_above": 256 } } }, "LASTUPDATED": { "type": "date" }, "LOCATION": { "properties": { "LAT": { "type": "float" }, "LON": { "type": "float" } } }, "PLACETYPE": { "type": "text", "fields": { "keyword": { "type": "keyword", "ignore_above": 256 } } }, "TIMESTAMP": { "type": "date" }, "TYPE": { "type": "text", "fields": { "keyword": { "type": "keyword", "ignore_above": 256 } } }, "location_example_01": { "type": "geo_point" }, "location_example_02": { "type": "geo_point" } } } } } -
View the data: